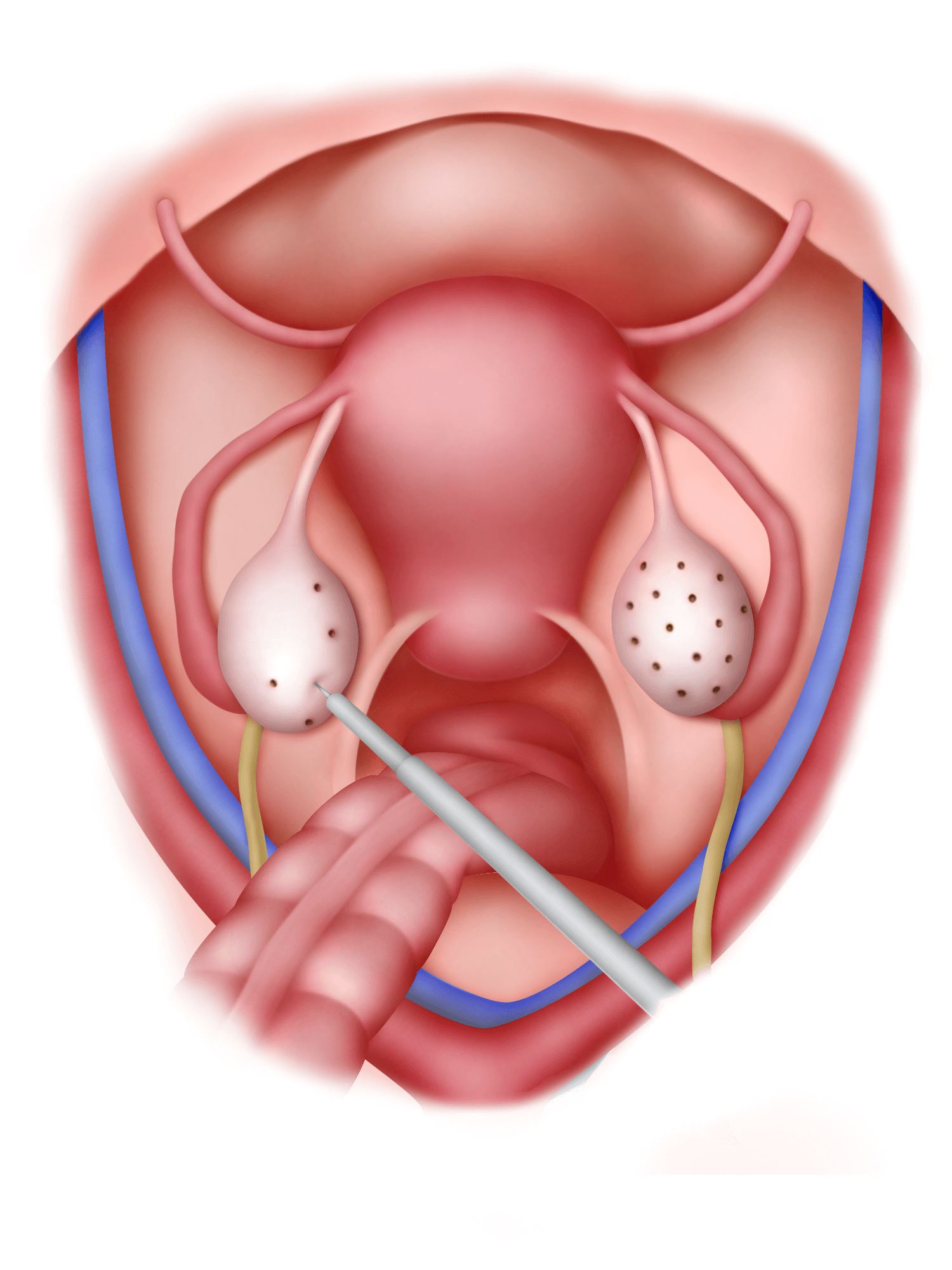
Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling
This surgery has been advocated for polycystic ovarian disease. It is performed in women who despite weight reduction and fertility drugs, still do not ovulate. The aim of this surgery is to destroy the ovarian capsule. This will reduce androgen (g) (male hormone) production and lead to regular ovulation and pregnancy.
How is it performed?
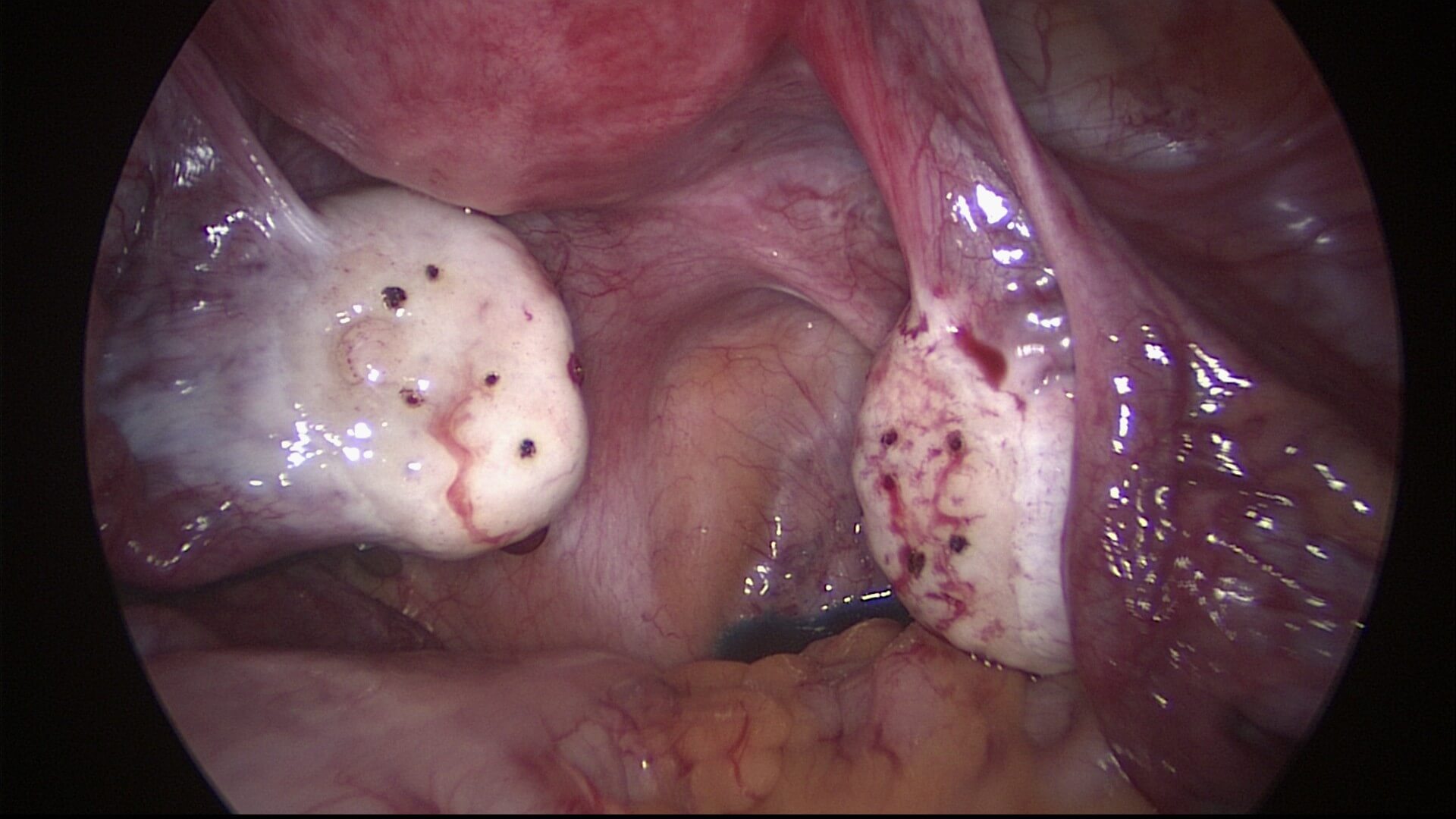
This surgery is usually performed with 3 incisions,. The first incision is in the umbilicus for the placement of the laparoscope. The second is to pass a grasper to hold the ovary and the third is to pass a “fine pin” needle diathermy instrument. This instrument is used to “drill” holes into the ovaries using electrical current. The number of holes made differ, ranging from 4 to 12. The duration of each drilling is
a few seconds. This surgery can also be performed using lasers.
Advantage
The advantage of this technique is that it is easy to perform and the reported ovulation rate post operation is 80% and pregnancy rate 50%.
Disadvantage
There is a risk of ovarian scarring, formation of adhesions and damage to the ovary and its blood supply leading to premature ovarian failure.

Summary
Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling is one
of the options often considered for the treatment of polycystic ovarian disease. It is an easy operation to perform but has a risk of premature ovarian failure
